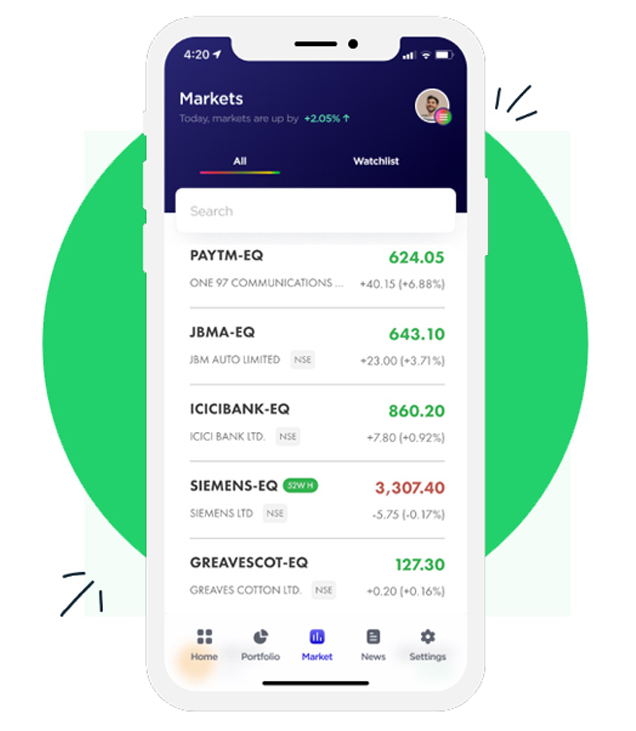
Stocks (Equity)
-
What is Equity?
Equity represents ownership in a company. When you buy stocks, you become a shareholder with potential for capital appreciation and dividends.
-
Trading Methods:
• Day Trading: Buying and selling within the same day
• Delivery Trading: Buying and holding for longer periods
• Swing Trading: Holding for days/weeks to capture price swings
• Position Trading: Long-term holding (months/years) -
How Equity Trading Works:
1. Open a demat and trading account
2. Fund your account
3. Research and select stocks
4. Place buy/sell orders through Billa Money’s trading platform
5. Settlement occurs through stock exchanges
Futures & Options (F&O)
-
Derivatives Trading
F&O are financial contracts that derive their value from an underlying asset (stocks, indices, commodities).
-
Futures
Binding contract to buy/sell asset at predetermined price on future date. Used for hedging or speculation with leverage.
-
Options
Gives right (not obligation) to buy/sell at strike price.
• Call Option: Right to buy
• Put Option: Right to sell -
Common Strategies
• Hedging: Reducing risk in existing positions
• Arbitrage: Profiting from price differences
• Straddle/Strangle: Volatility plays
• Spread Strategies: Using multiple options

Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs)
-
What are ETFs?
Baskets of securities that trade on exchanges like stocks, offering diversification at lower costs.
-
How ETF Trading Works:
1. Traded throughout market hours like stocks
2. No minimum investment requirement
3. Lower expense ratios than mutual funds
4. Transparent holdings (usually index-based) -
Popular ETFs in India:
• Nifty 50 ETFs
• Gold ETFs
• Sectoral ETFs (Banking, IT, etc.)
• International ETFs
• Bond ETFs
Mutual Funds (MF)
-
Pooled investments managed by professionals, offering diversified portfolios.
-
Types of Mutual Funds:
• By Structure: Open-ended, Close-ended, Interval
• By Asset Class: Equity, Debt, Hybrid, Solution-oriented
• By Investment Goal: Growth, Income, Tax-saving (ELSS)
• Sectoral/Thematic: Focused on specific sectors
• Index Funds: Tracking market indices

Initial Public Offering (IPO)
-
When a private company offers shares to the public for the first time.
-
IPO Process:
1. Company files draft prospectus with SEBI
2. Price band announcement
3. Subscription period (3-5 days)
4. Allotment and listing on exchanges -
Types of IPOs:
• Fixed Price: Predetermined price
• Book Building: Price discovery through bids
• OFS (Offer for Sale): Existing shareholders sell
Insurance Products
-
Financial protection against risks with investment components in some cases.
-
Major Insurance Types:
• Life Insurance: Term, Whole Life, Endowment, ULIPs
• Health Insurance: Mediclaim, Critical Illness, Top-up
• General Insurance: Motor, Home, Travel
• Annuities: Pension products -
Benefits:
• Risk coverage
• Tax benefits under Section 80C and 80D
• Long-term savings (for investment-linked products)

